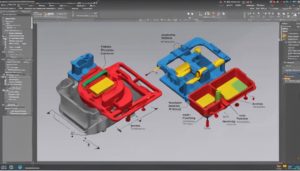
Injection molding manufacturing works by melting plastic pellets and injecting them into a mold cavity under high pressure. The plastic is then cooled and solidified to form the desired part. Precision control of temperature, pressure, and cooling guarantees high-quality and consistent output. The process involves mechanical force application to push the molten plastic into the mold for accurate part replication. This method is essential for mass production in various industries due to its efficiency and ability to produce intricate designs. Understanding each step in detail allows for best part formation and quality. Learn more about this intricate process to grasp its full complexity.
Injection Molding Process Overview
The injection molding process, a fundamental manufacturing technique, involves the precise melting of plastic pellets and their subsequent injection into a mold cavity to produce intricately shaped parts efficiently and consistently.
The mold used in injection molding is an essential component as it determines the final shape of the parts being produced. The material chosen for the mold must possess high heat resistance and durability to withstand the repeated cycles of heating and cooling during the manufacturing process.
Additionally, the material being injected into the mold plays a critical role in the quality of the final parts. It must have the necessary properties to flow easily into the mold cavity, solidify quickly, and exhibit the desired characteristics once cooled.
The parts produced through injection molding can vary greatly in complexity, from simple geometric shapes to intricate designs with fine details. This process is favored in industries where mass production of high-quality parts is required, such as automotive, medical devices, and consumer products.
Heating and Melting Plastic Material
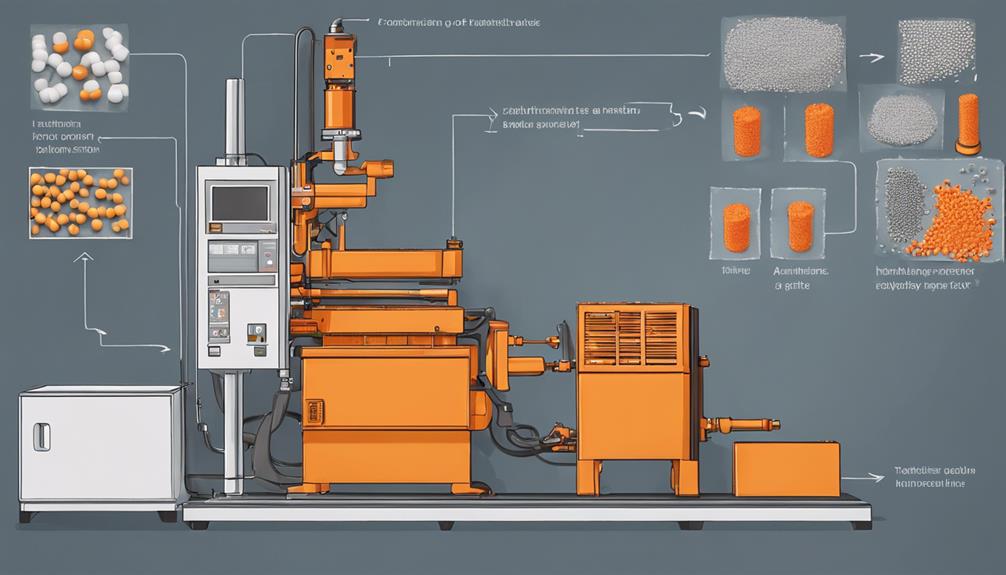
Heating and melting plastic material in the injection molding process involves subjecting the plastic pellets to controlled temperatures within the machine's heated barrel until they reach a molten state suitable for injection. The process of heating and melting plastic material is important in injection molding, ensuring the plastic can flow smoothly into the mold cavity and take on the desired shape.
Here are some key points to keep in mind:
- Temperature Control: The temperature range for melting plastic material typically falls between 200°C to 300°C, depending on the type of resin being used. Precise temperature control is crucial to achieve the correct viscosity for injection.
- Avoiding Degradation: Consistent heating is essential to prevent material degradation during the melting process. Maintaining the plastic at the correct temperature helps ensure the integrity of the material is preserved.
- Quality Assurance: Achieving a uniform molten state for the plastic material is important to produce high-quality molded parts. Proper heating and melting of the plastic material contribute to the final product's accuracy and structural integrity.
Injecting Plastic Into Mold
To initiate the injection process of plastic into the mold cavity, precise control of pressure is utilized to guarantee accurate and complete filling. The plastic is injected through a gate into the mold cavity, ensuring that it takes the shape of the mold accurately. This process is essential in achieving the desired part without defects. Injection speed and pressure are adjusted carefully to prevent issues such as voids or warping that could compromise the quality of the final product. Cooling systems play an important role in solidifying the molten plastic inside the mold, allowing for proper part formation. Once the plastic has solidified, the mold opens, and the finished part is ejected for further processing or assembly.
| Key Aspects | Details |
|---|---|
| Injection Process | Plastic injected into mold cavity through gate |
| Pressure Control | Ensures complete filling of mold |
| Cooling Systems | Solidify molten plastic for part formation |
| Defect Prevention | Adjusted speed and pressure to avoid voids or warping |
High-Pressure Molding
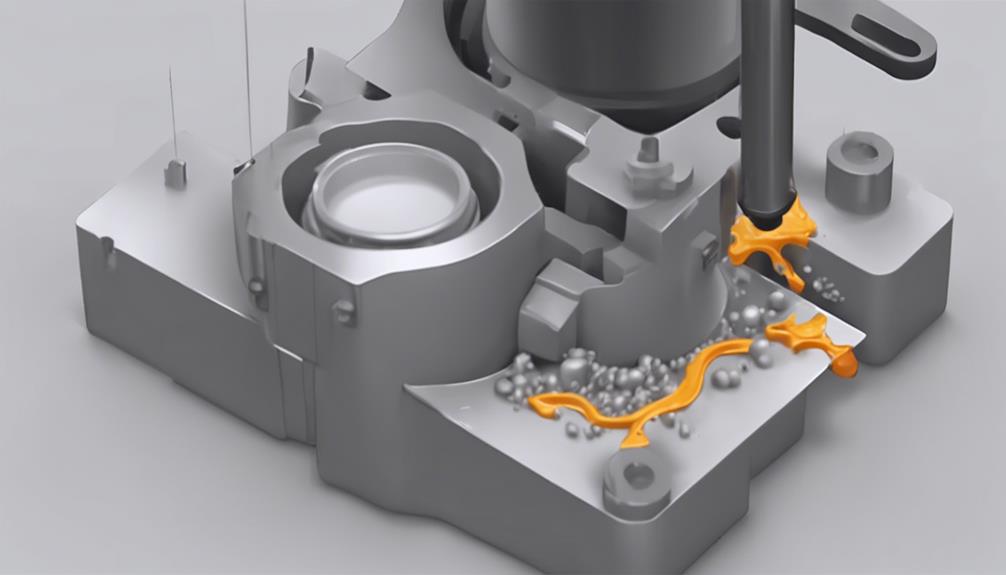

Utilizing significant force, high-pressure molding involves injecting molten material into a mold cavity to guarantee precise material flow and complete mold filling. This process is vital in ensuring the production of high-quality plastic parts.
Here are key points to ponder in high-pressure molding:
- Injection Pressure: High-pressure molding typically operates within a range of 500 to 1500 bar. This high injection pressure is essential to overcome the viscosity of the molten material and facilitate its flow into intricate mold cavities with precision.
- Clamping Force: The clamping force applied during high-pressure molding is crucial for maintaining the structural integrity of the mold. It ensures that the mold remains securely closed throughout the injection process, preventing any material leakage or deformation of the final part.
- Nozzle Pressure Control: Precise control of the nozzle pressure is crucial in high-pressure molding. Maintaining consistent nozzle pressure helps regulate the flow rate of the molten material, contributing to the uniformity and quality of the injected parts.
Cooling and Solidification Stage
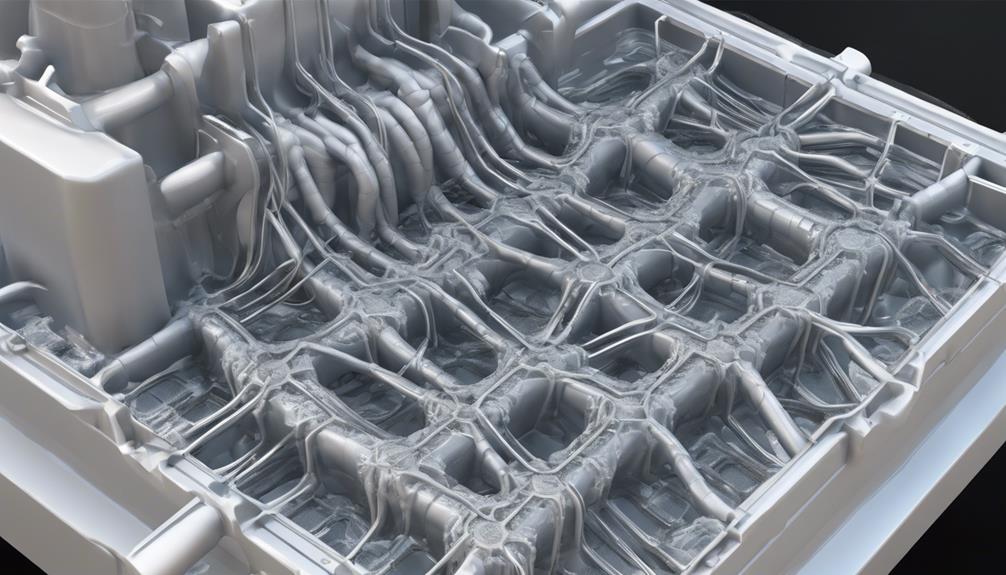

During the cooling and solidification stage in injection molding, the controlled extraction of heat from the molten plastic is essential to guarantee proper part formation and dimensional accuracy.
The cooling time plays a significant role in determining the final strength and dimensional accuracy of the molded part. Efficient cooling helps prevent common defects such as warping, shrinkage, and internal stresses in the component.
Cooling channels integrated within the mold aid in the uniform cooling of the plastic part, ensuring consistent quality throughout. Proper temperature control during cooling is vital to achieve the desired material properties and part specifications.
Ultimately, the cooling and solidification stage is a critical phase in the injection molding process, influencing the final strength of the part and ensuring it meets the required design standards.
Mold Opening and Ejection
Following the completion of the cooling and solidification stage in injection molding, the next critical phase is the precise opening of the mold for the ejection of the solidified plastic part. This step is important to guarantee the efficient release of the part without causing any damage to the mold or the part itself. The mold opening and ejection process involve the following key components and actions:
- Ejection Pins: These are mechanical components within the mold that are activated to push the solidified plastic part out of the mold cavity. The design and placement of ejection pins are essential to achieve a clean and successful ejection process.
- Ejection Mechanisms: Hydraulic or mechanical systems are utilized to open the mold with precision and control. These mechanisms ensure that the mold halves separate smoothly and consistently, allowing for the easy removal of the part.
- Damage Prevention: Proper ejection mechanisms are crucial to prevent any damage to the part or the mold during the ejection process. Careful consideration of the ejection system is necessary to maintain the quality of the final product and the longevity of the mold.
Mechanical Force Application
After the completion of mold opening and ejection, the injection molding process moves to the critical stage of applying mechanical force to push molten plastic into the mold cavity. This force application is a vital step in ensuring the production of high-quality parts.
The injection molding machine exerts controlled force to facilitate the complete filling of the mold, which is essential for accurate and defect-free parts. Proper management of the force is necessary to prevent issues such as voids or short shots in the molded components.
The force applied during molding plays a significant role in determining the final part's dimensions, surface finish, and overall quality. By understanding and controlling the mechanical force effectively, manufacturers can achieve consistent and reliable results in injection molding production.
Attention to detail in force application is paramount for the successful creation of intricate and flawless plastic parts.
Production of Plastic Parts
Plastic parts are manufactured through the injection molding process by melting plastic resin pellets and injecting them into a mold cavity. This method of manufacturing plastic parts involves several vital steps:
- Molten Plastic Formation: The thermoplastic material is heated to a molten state within the injection molding machine. The plastic resin pellets are melted under high temperatures to achieve the desired viscosity for injection into the mold cavity.
- Injection into Mold Cavity: The molten plastic is injected into the mold cavity under high pressure. The mold is designed to shape the plastic into the desired form, whether it be intricate geometries or simple shapes.
- Cooling and Solidification: Once the molten plastic fills the mold cavity, it is cooled and solidified to take on the shape of the mold. Cooling time is critical to make sure the part sets properly and maintains its structural integrity.
This precise process enables the production of high-quality plastic parts with consistency and accuracy, making injection molding a preferred method for manufacturing plastic components in various industries.
Importance of Precision in Molding
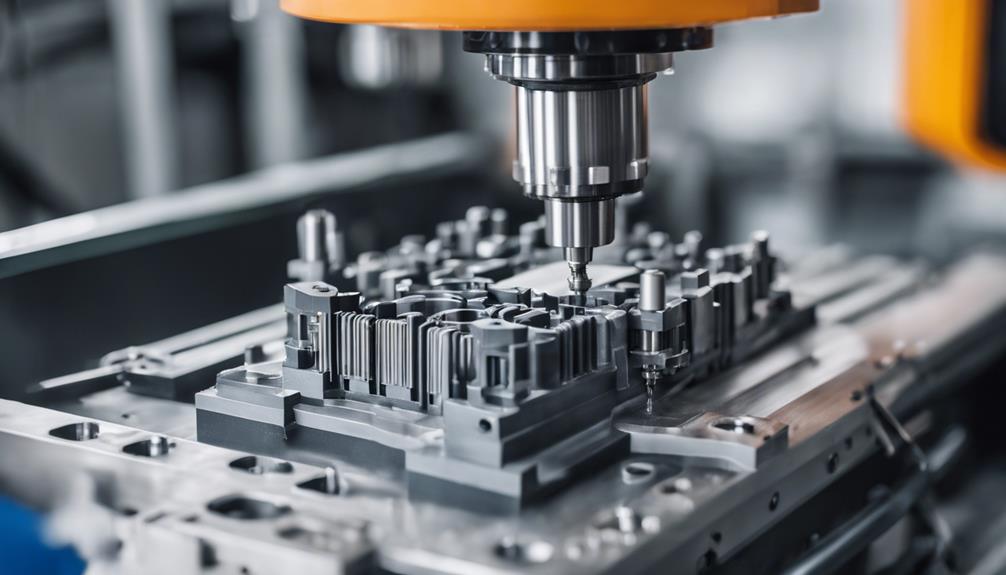

Precision in molding plays a fundamental role in ensuring the accurate replication of intricate designs and maintaining consistent dimensions in plastic part production. Achieving tight tolerances in injection molding processes is essential for producing high-quality and uniform products consistently.
By maintaining precision throughout the molding operations, the need for post-production adjustments or rework is greatly reduced, resulting in time and cost savings. Advanced technologies such as computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) are instrumental in enhancing precision in molding processes.
Quality control measures like statistical process control (SPC) are implemented to monitor and uphold precision at every stage of the molding process. Overall, precision in molding is critical for meeting design specifications, ensuring product quality, and optimizing production efficiency.
Ensuring Quality in Manufacturing
Quality control measures and defect prevention strategies play a crucial role in ensuring the high standards of injection molding manufacturing. By implementing rigorous inspection processes and adhering to industry standards like ISO 13485, manufacturers can guarantee the quality and precision of their molded products.
Continuous monitoring and adjustment of process parameters are key to maintaining consistency and reliability in injection molding production.
Quality Control Measures
Implementing stringent quality control measures is essential in injection molding to uphold manufacturing standards and guarantee product integrity. Quality control in injection molding involves various inspection methods to make sure the produced parts meet specified criteria.
Three key aspects of quality control measures in injection molding include:
- Visual Inspection: Visual inspection is vital in identifying surface defects like scratches, discoloration, or flash.
- Dimensional Measurement: Using precise tools, dimensional measurements are taken to verify that parts meet exact specifications.
- Material Testing: Conducting material testing ensures that the materials used in the molding process meet the required standards for strength, durability, and other properties.
Defect Prevention Strategies
To uphold the integrity of manufactured parts in injection molding, effective defect prevention strategies are essential in maintaining high-quality standards throughout the production process. Proper mold design with adequate draft angles and venting is vital in preventing defects. Venting allows for the release of air and gases during the injection process, reducing the likelihood of imperfections.
Quality control measures such as monitoring injection pressure, temperature, and using quality materials are indispensable. Conducting regular maintenance on machines ensures peak performance and helps prevent defects.
Rigorous quality control, including visual inspections and testing, helps in identifying and rectifying defects early.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Does Injection Molding Work Step by Step?
Injection molding works by melting plastic resin pellets in a heated barrel, then injecting the molten plastic into a mold cavity under pressure.
The plastic cools and solidifies in the mold, taking the desired shape.
Finally, the molded part is ejected from the mold using an ejection system.
This process demands precise control of parameters like temperature, pressure, and cooling time to guarantee the production of high-quality parts.
What Is the Manufacturing Process of Injection Molding Machine?
The manufacturing process of an injection molding machine involves the precise feeding of plastic pellets into a heated barrel where they are melted under high pressure.
The molten plastic is then injected into a mold cavity to form the desired shape.
Cooling the mold solidifies the plastic before ejection of the final product.
This method guarantees consistent and accurate production of plastic parts through a controlled and repeatable process.
How Is an Injection Mold Made?
An injection mold is made through a process involving the design and fabrication of two main components: the cavity and the core. These components are typically constructed from steel or aluminum using CNC machining or electrical discharge machining (EDM) for accuracy.
Factors such as cooling channels, ejection systems, and parting lines are carefully considered during the design stage to guarantee efficient production. Proper maintenance of the mold is essential for consistent part quality and longevity.
What Are the Four Stages of Injection Molding?
The four stages of injection molding encompass feeding and melting thermoplastic, injecting the material into the mold, holding and cooling it, and ejecting the finished parts. This process guarantees precise and efficient fabrication of plastic components.
Each stage plays a critical role in achieving high-quality results. From initial material preparation to final product extraction, adherence to these stages is key to successful injection molding production.
Conclusion
In summary, the injection molding manufacturing process involves heating and melting plastic material, injecting it into a mold under high pressure, and cooling it to solidify the desired shape.
Precision and quality control are essential in ensuring the production of accurate plastic parts.
The theory that injection molding is a precise and efficient manufacturing method has been proven through the consistent production of high-quality plastic products.