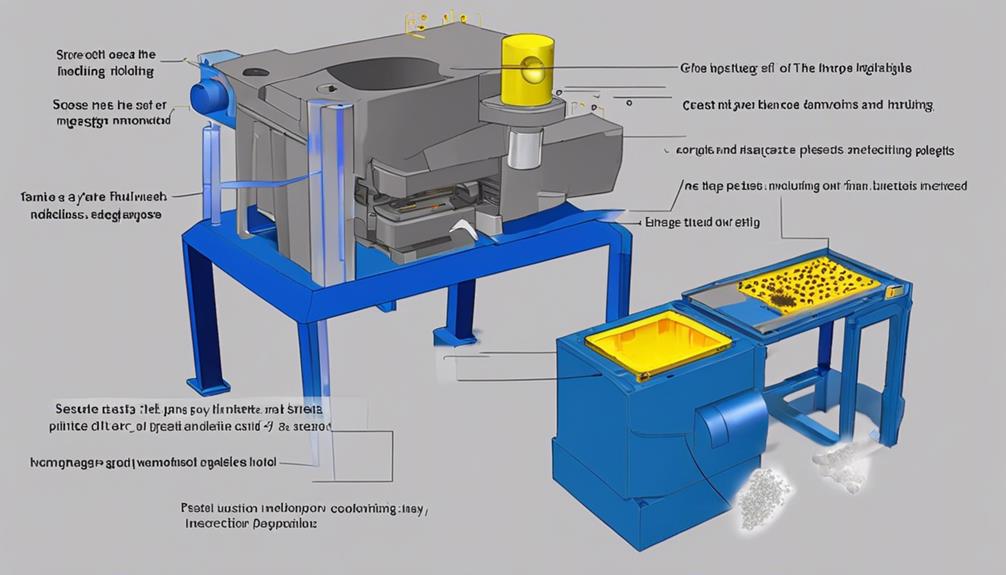
Mastering injection molding basics is essential for beginners entering the domain of this efficient manufacturing process. It involves intricate steps like high-pressure injection, molten plastic injection into metal molds, and precise cooling for solidification. Understanding types of molding such as thermoplastic and overmolding, design principles like wall thickness and draft angles, and selecting resins and additives are key aspects. Quality systems like ISO 13485 compliance and first article inspection are paramount. Further, exploring online courses like 'Fundamentals of Injection Molding' and industry events such as NPE: The Plastics Show provide deeper insights into this field.
Understanding Injection Molding Basics
Injection molding is a highly efficient manufacturing process that involves injecting molten plastic into a precisely designed metal mold cavity to produce intricate plastic parts with exceptional accuracy.
The process encompasses the use of various materials, such as plastic resin pellets, which are heated and melted in the injection unit's heated barrel. Once in a molten state, the plastic is injected into the mold cavity through a combination of pressure and speed, ensuring the material takes the shape of the mold accurately.
The mold, an essential component in injection molding, is intricately designed to create the desired part geometry. Cooling channels within the mold aid in the solidification of the molten plastic, allowing it to retain the intended shape.
Injection molding is a widely utilized manufacturing process due to its ability to produce high volumes of parts with consistent quality, making it a preferred choice across industries for creating complex shapes with precision.
Working Mechanism of Injection Molding
Utilizing precise control and intricate design, the working mechanism of molding plastic through high-pressure injection involves a meticulous interplay of components within the injection molding machine.
The injection molding process begins with the injection unit melting the raw material, typically plastic resin, into a molten state. This molten plastic material is then injected into a metal mold through the mold cavity under high pressure. The mold cavity is the space where the molten plastic fills and takes the shape of the final product.
Cooling channels within the mold help cool and solidify the plastic swiftly, allowing for efficient production cycles. The clamping unit of the machine makes certain that the mold stays closed during injection to prevent any deformities in the final product.
This intricate process results in the creation of a precise and high-quality plastic part through the controlled application of pressure and temperature within the injection molding machine.
Types of Injection Molding

In the field of injection molding, understanding the various types is essential for producing quality parts. Common molding methods encompass thermoplastic, liquid silicone rubber, overmolding, and insert molding, each tailored to specific material properties and part requirements.
Common Molding Methods
Among the various molding methods employed in manufacturing processes, a range of common types of injection molding techniques are utilized to produce intricate and functional components.
- Thermoplastic molding: Widely used for its versatility and cost-effectiveness.
- Liquid silicone rubber molding: Ideal for producing flexible and heat-resistant parts like seals and gaskets.
- Overmolding: Involves molding one material over another, creating a seamless bond for products like handles and grips.
- Insert molding: Integrates metal or plastic inserts into the mold, providing strength and functionality to the final part.
Materials Used
Injection molding relies heavily on the selection of appropriate materials to achieve desired part characteristics. Common options include thermoplastics like ABS, polycarbonate, and polypropylene. Specialty materials such as nylon, acrylic, and polystyrene are also favored for specific applications. High-performance engineering plastics like PEEK, PPS, and Ultem are utilized for demanding environments. Additives such as glass fibers, minerals, and flame retardants can be incorporated to enhance material properties based on specific requirements. Material selection plays an essential role in determining part characteristics such as strength, flexibility, and heat resistance in injection molding processes. This ensures that the final product meets the necessary specifications for its intended use.
Process Steps
The process steps in injection molding encompass a series of precisely orchestrated procedures aimed at transforming resin pellets into finished parts with meticulous accuracy and efficiency.
- Thermoplastic Molding: Common method involving melting and reshaping plastic under heat and pressure.
- Liquid Silicone Rubber Molding: Utilized for flexible parts like seals and gaskets, offering high precision and durability.
- Overmolding: Technique allowing for combining different materials during the molding process for complex part designs.
- Insert Molding: Process enabling the incorporation of various components into the mold to create intricate plastic parts.
Design Principles for Injection Molding
What key considerations should be accounted for when designing parts for injection molding processes to guarantee successful production outcomes?
Design principles in injection molding play an essential role in ensuring the quality and efficiency of the manufacturing process. Factors such as wall thickness, draft angles, core geometry, tolerances, and defect prevention are important in the design phase to achieve favorable results.
Maintaining uniform wall thickness is necessary for part strength, appearance, and minimizing defects like sink marks and warping. Draft angles are required to facilitate easy ejection of the part from the mold without causing damage.
Core geometry design influences the complexity of the part shape and the effectiveness of the molding process. Attention to tolerances is crucial to meet dimensional requirements for functional and aesthetic purposes in the final molded part.
Injection Molding Resins and Additives

When designing parts for injection molding processes, the selection of appropriate resins and additives is essential to guarantee ideal material properties and successful production outcomes. Injection molding resins such as ABS, PET, and polycarbonate are chosen based on factors like melting temperature and flow rate, ensuring proper molding conditions.
Additives play a significant role in enhancing material properties, with options like short glass fibers, talc, and clay being commonly used. These additives can improve aspects such as strength, stiffness, impact resistance, and flame retardancy, tailoring the material to specific application requirements.
Additionally, colorants are frequently incorporated into resins to achieve desired colors in the final molded parts, adding a visual element to the functional properties of the components. Careful consideration of both resins and additives is vital in achieving the desired material characteristics and ensuring the successful production of high-quality injection molded parts.
Surface Finishes for Molded Parts

Surface finishes in injection molding encompass various techniques aimed at enhancing the aesthetics and functionality of molded parts. Textured surfaces can cater to specific design requirements, providing a unique look and feel to the final product. Ultrasonic welding guarantees seamless connections between plastic parts, offering strong and durable joints. Pad printing allows for intricate designs to be added to molded parts, ideal for branding or labeling purposes. Laser engraving provides precise and permanent markings on the surface of molded parts, adding a professional and customized touch.
| Technique | Description | Application |
|---|---|---|
| Textured Surfaces | Provide unique feel and appearance | Aesthetics, design requirements |
| Ultrasonic Welding | Join plastic parts seamlessly | Ensuring strong and durable connections |
| Pad Printing | Add detailed designs to parts | Branding, labeling purposes |
| Laser Engraving | Offer precise and permanent markings | Professional touch, customization |
Quality Systems in Injection Molding

The implementation of quality systems in injection molding plays a vital role in ensuring the consistency and adherence to industry standards for producing high-quality parts. Quality systems in injection molding encompass various aspects essential for achieving precision and reliability in part production:
- ISO 13485 Compliance: Ensuring that the manufacturing processes meet the stringent requirements set by the ISO standard for medical applications.
- Scientific Molding Techniques: Employing standardized methods based on scientific principles to optimize processes and achieve defect-free parts consistently.
- First Article Inspection (FAI): Conducting thorough inspections of the initial parts to verify that they meet all specifications before proceeding with mass production.
- Production Part Approval Process (PPAP): Following a standardized approach to approving parts for production, ensuring that all requirements are met before full-scale manufacturing begins.
Quality control systems are paramount for maintaining product consistency and meeting the demands of industries such as medical devices, automotive, and consumer products. By integrating these quality systems, manufacturers can uphold high standards and deliver reliable products to their customers.
Additional Resources for Injection Molding

When seeking additional resources for injection molding, exploring useful online courses and industry events listings can provide valuable insights and knowledge.
Online platforms offering interactive quotes and free DFM analysis for 3D CAD models can assist in understanding the manufacturing process better.
Consulting experienced applications engineers or technical support services like Protolabs can offer guidance and feedback essential for successful production outcomes.
Useful Online Courses
For individuals seeking to enhance their understanding of injection molding processes and materials, exploring online courses such as 'Fundamentals of Injection Molding' on Coursera can provide valuable insights. These courses cover a wide range of topics related to injection molding, including:
- 'Injection Molding Basics' on Udemy: Tooling fabrication, part production steps, and quality control systems.
- 'Mastering Injection Molding Techniques' on LinkedIn Learning: Design principles, surface finishes, and material selection.
- 'Advanced Injection Molding Strategies' on Skillshare: Specialty techniques like overmolding and insert molding.
- 'Injection Molding for Beginners' on Pluralsight: Thorough overview of injection molding operation and industry applications.
Industry Events Listing
Exploring a wide range of industry events can greatly enhance one's knowledge and understanding of the latest trends and innovations in injection molding.
Events like NPE: The Plastics Show and K Trade Fair serve as platforms for networking and showcasing cutting-edge injection molding technologies.
Additionally, conferences such as Molding Conference and Injection Molding and Design Expo offer valuable insights into industry advancements.
Trade shows like Plastec West and Expoplast provide opportunities for beginners to learn about new materials, machinery, and processes in the field.
Furthermore, workshops and seminars at Amerimold and Plastics Technology Expo offer hands-on learning experiences for novices.
These industry events feature expert speakers, live equipment demonstrations, and panel discussions, making them essential resources for staying abreast of developments in injection molding.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are the Basics of Injection Molding?
Injection molding basics encompass the process of injecting molten plastic into a mold cavity to create plastic parts. This involves melting plastic resin pellets in a heated barrel before injection.
Key components of injection molding machines include the injection unit and clamping unit.
Mold cavity design plays an important role in shaping the molten plastic material into the desired part.
Different plastic materials like ABS, PET, and polycarbonate are commonly used in injection molding for various applications.
What Are the 5 Steps of Injection Molding?
The five key steps of injection molding are clamping, injection, dwelling, cooling, and ejection.
Clamping secures the mold, injection fills it with molten plastic, dwelling allows for cooling, and ejection releases the final part.
Each step is vital for producing high-quality parts efficiently. Proper timing and control of these steps are essential for consistent part quality and successful production.
Beginners must understand and master these steps to excel in the field of injection molding.
What Are the 4 Stages of Injection Molding?
The 4 stages of injection molding are:
- Clamping secures the mold during injection to prevent material leakage.
- Injection involves melting and injecting plastic into the mold.
- Cooling allows the material to solidify.
- Ejection releases the finished part from the mold.
For instance, in automotive manufacturing, these stages are essential for producing precise and durable components like engine mounts or interior trim pieces.
What Are the Basic Principles of Injection Moulding?
The fundamental principles of injection molding involve the precise injection of molten material into a mold cavity under high pressure to form intricate plastic parts. Key considerations include mold design, material selection, and processing parameters to guarantee quality and efficiency. Proper cooling and ejection mechanisms are critical for part release and dimensional accuracy.
Mastering these principles is essential for achieving consistent and reliable production outcomes in various industries.
Conclusion
To sum up, mastering injection molding basics is like laying the foundation for a solid structure. Just as each component in a building must be carefully crafted and assembled to guarantee stability and strength, understanding the intricacies of injection molding is essential for producing high-quality parts.
By following the principles outlined in this guide, beginners can embark on their journey towards becoming proficient in this complex yet rewarding manufacturing process.