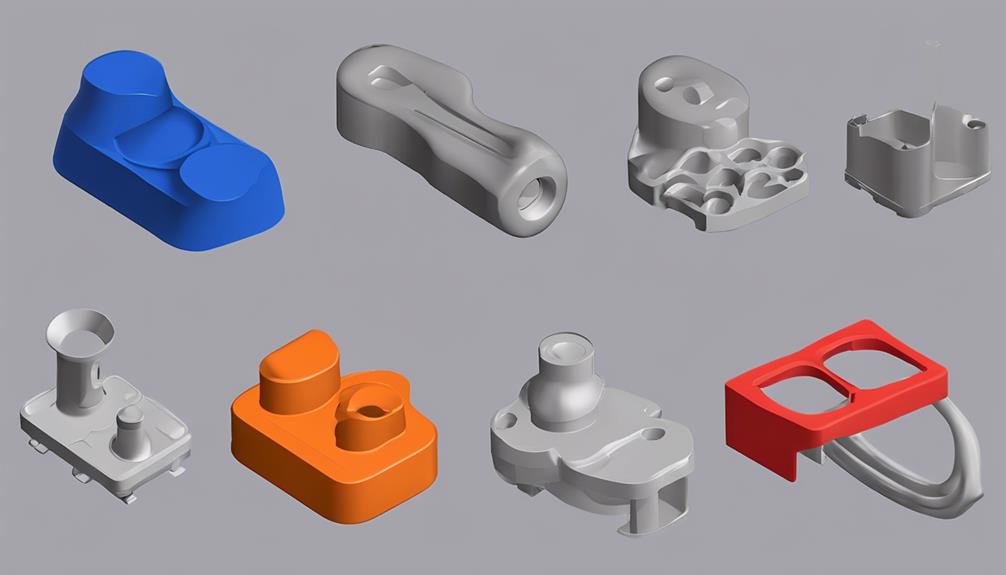
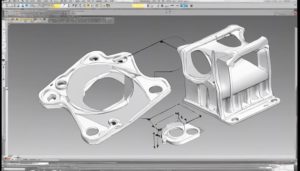
To master injection molding as a beginner, start by grasping the detailed process that involves precise plastic injection into molds for producing intricate parts at high volumes. Understand the key components like the injection unit, mold, and clamping unit. Consider design elements such as tolerances, material selection, and mold design for quality outcomes. Pay attention to surface finishes and implement quality systems for reliability. Knowing how to select resins and apply scientific molding techniques is essential. Mastering injection molding demands a thorough understanding of its nuances and applications. Continue exploring to enhance your expertise in producing top-quality plastic parts.
Basics of Injection Molding
Injection molding is a fundamental process in manufacturing. It involves the precise injection of molten plastic into molds to create solid parts. This method is widely used due to its ability to produce high volumes of parts with intricate designs and excellent repeatability.
The process begins with feeding plastic material into the machine, where it is melted in a heated barrel before being injected into mold cavities under high pressure. Mold design is pivotal in determining the final shape and features of the part, making it a critical aspect of the injection molding process.
Proper material selection, machine setup, cooling, and ejection are also essential steps for successful part production. Injection molding is favored in various industries such as medical devices, consumer products, and automotive components due to its efficiency and cost-effectiveness in mass production.
Understanding the basics of injection molding is key to mastering this manufacturing process and achieving high-quality results.
Understanding Injection Molding Process
The understanding of the injection molding process begins with a detailed overview of its intricacies, including the sequence of steps involved in creating a molded part. Key components such as the injection unit, mold, and clamping unit play vital roles in ensuring the process's success by facilitating the precise injection of molten material under controlled conditions.
The injection cycle encompasses the stages of filling, packing, cooling, and ejection, each requiring meticulous monitoring to achieve the desired part quality and dimensional accuracy.
Process Overview
In the domain of plastic manufacturing processes, the intricate dance of material transformation unfolds within the confines of an injection molding machine. The process begins with the feeding of plastic pellets into the machine, where they are heated and melted.
The molten material is then injected into a mold cavity to form the desired shape of the part. The cooling process follows, during which the material solidifies within the mold. Once cooled, the final part is ejected from the mold, ready for further processing or use.
Injection molding enables efficient production of parts with high precision and repeatability, making it a preferred method in industries such as automotive, medical devices, consumer products, and packaging.
Key Components
Within the domain of plastic manufacturing processes, understanding the intricacies of injection molding necessitates a thorough grasp of the key components involved in shaping the final product.
The mold plays a critical role in determining the final shape of the part, while the injection unit is responsible for melting and injecting the material into the mold cavity.
The clamping unit guarantees proper alignment of the mold halves during the injection molding process.
Material preparation is a vital step that involves resin selection, drying, heating, and mixing to achieve the desired properties in the final part.
Injection molding is favored in various industries like automotive, consumer goods, packaging, and medical devices due to its efficiency and versatility in producing high-quality parts.
Injection Cycle
Efficient execution of the injection cycle is fundamental to achieving precise and consistent outcomes in the intricate process of injection molding. The injection process involves clamping the mold, injecting molten plastic, initiating the cooling phase, and ejecting the final product.
Each stage is crucial for guaranteeing the production of high-quality parts. Proper adjustment of machine parameters, such as temperature, pressure, and speed, during the injection cycle is essential to secure ideal material flow and part formation.
The cooling phase plays a critical role in determining the final part's shape, dimensions, and structural integrity. Understanding and mastering the injection cycle not only lead to high-quality parts but also optimize production efficiency, reduce defects, and ensure successful molding outcomes.
Design Principles for Molding
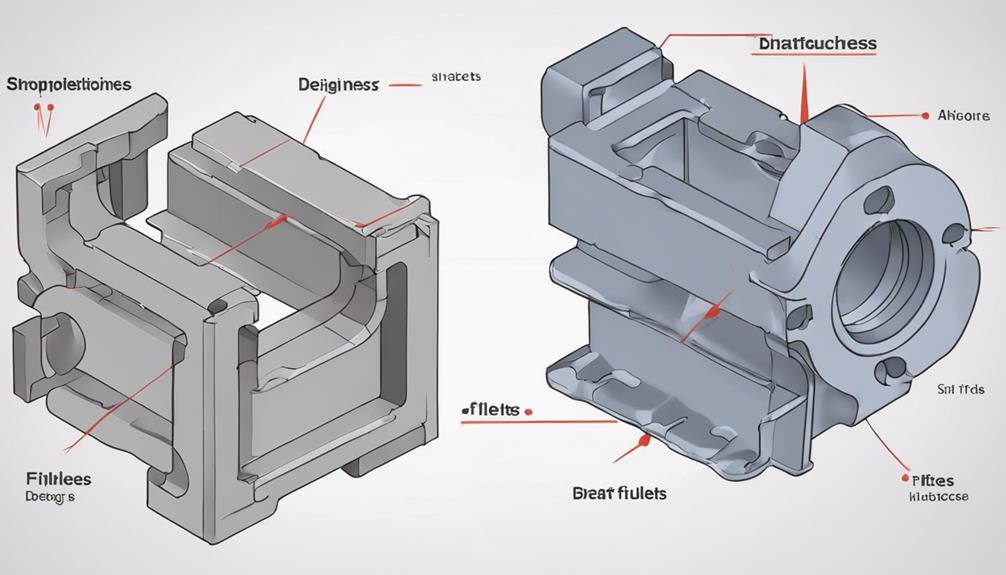
Design principles for molding are essential in ensuring the accuracy and quality of produced parts. Considerations such as tolerances, wall thickness, core geometry, and draft angles play pivotal roles in the molding process.
Mold Design Basics
Considering factors such as tolerances, wall thickness, core geometry, and draft angles is essential to guarantee successful molding in injection molding processes. Mold design plays a pivotal role in ensuring high part quality, efficient material flow, and ideal cooling time.
Structural integrity is enhanced by incorporating features like ribs, fillets, and bosses in the mold design. Advanced software tools enable simulation and optimization of the molding process, aiding in achieving superior results.
Material Selection Tips
Material selection in injection molding is a critical aspect that profoundly influences the mechanical and chemical properties of the final part. When choosing materials for injection molding, consider the following key points:
- Consider Thermoplastics: Common thermoplastics like polypropylene, polyethylene, ABS, and polycarbonate offer different properties suitable for various applications.
- Evaluate Chemical Resistance: Factor in the material's resistance to chemicals, guaranteeing it can withstand the intended environment.
- Utilize Fillers: Incorporating fillers such as glass fibers, minerals, or additives can enhance material properties, improving strength or other characteristics as needed.
Material selection should align with mold design, processing conditions, and part geometry to secure successful injection molding outcomes.
Draft Angle Importance
Draft angles play an important role in injection molding processes by ensuring the smooth ejection of parts from the mold. Adequate draft angles are essential as they help prevent part damage or sticking in the mold, ultimately impacting production efficiency.
Typically recommended at 1 to 3 degrees per side, draft angles aid in reducing friction between the part and mold, thereby decreasing the likelihood of surface defects and enhancing overall quality. Additionally, these angles assist in minimizing the risk of warping or distortion in the molded part during the cooling phase.
Selecting Injection Molding Resins

When selecting resin for injection molding, it is important to take into account properties such as strength, flexibility, and heat resistance to guarantee the desired characteristics of the final molded part.
- Thermoplastic Resins: Common thermoplastic resins like ABS, polypropylene, and polycarbonate are popular choices due to their versatility and ease of molding.
- Specialized Resins: Specialized resins cater to specific needs, offering solutions for applications requiring high-temperature resistance or exceptional chemical resistance.
- Impact on Properties: The selection of resin has a significant effect on the mechanical, thermal, and aesthetic qualities of the molded parts. Understanding these properties is essential for achieving the desired durability, appearance, and performance characteristics in the final product.
Careful consideration of resin selection ensures that the molded parts meet the necessary requirements for the intended application, whether it be regarding strength, appearance, or resistance to external factors.
Achieving Surface Finishes

To achieve a range of surface finishes in injection molding, meticulous attention to mold materials selection and precision polishing techniques is essential. Surface finishes can vary from high gloss to matte and textured finishes, each requiring specific approaches. The choice of mold materials plays a vital role in determining the final appearance of the molded part.
Polishing techniques are necessary for achieving desired surface finishes, whether it is a smooth, polished, matte, or patterned look. High gloss finishes are typically achieved through meticulous polishing of the mold surface, while matte finishes may require different texturing methods. Textured finishes add a tactile dimension to the part, enhancing both its appearance and functionality.
The surface finish of a molded part can profoundly impact its overall aesthetics and perceived quality. By carefully selecting mold materials and employing appropriate polishing techniques, manufacturers can customize and enhance the surface finishes of injection-molded products to meet specific design requirements.
Implementing Quality Systems

Injection molding manufacturers must implement robust quality systems to guarantee consistency, reliability, and high standards in the production processes. To achieve this, the following key steps should be considered:
- Implement Scientific Molding Techniques: Utilizing scientific molding principles helps standardize production parameters such as temperature, pressure, and cooling rates, leading to optimized part quality and process efficiency.
- Conduct First Article Inspection (FAI) and Production Part Approval Process (PPAP): These procedures are essential quality control measures to validate that the initial parts meet all specified requirements before full production runs, ensuring product conformity and minimizing defects.
- Compliance with ISO 13485: For manufacturers serving the medical industry, adherence to ISO 13485 standards is critical. This certification ensures that the quality management systems in place meet the stringent requirements for medical device production, emphasizing safety and effectiveness.
Online Injection Molding Quote
Acquire instant cost estimates for your injection molding needs through an online quoting system, facilitating efficient project planning and decision-making. Online injection molding quotes offer a streamlined approach to evaluating project requirements, providing insights into materials, processes, and lead times.
By utilizing this tool, individuals can promptly compare pricing and services from various providers, aiding in well-informed decision-making. This online resource serves as a valuable asset in injection molding project planning, allowing for quick and accurate budget estimations.
Additionally, the accessibility of online injection molding quotes enhances the overall efficiency of the procurement process, enabling businesses to make data-driven choices. Leveraging this digital solution not only expedites cost calculations but also assists in understanding the intricacies of injection molding services, promoting a thorough grasp of the project scope.
Ultimately, the utilization of online quoting systems for injection molding aligns with contemporary industry practices, emphasizing convenience and precision in cost estimation and project planning.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are the 5 Steps of Injection Molding?
The 5 key steps of injection molding are:
- Mold preparation involves ensuring the mold is clean and ready for use.
- Material selection is essential for achieving the desired properties in the final part.
- Machine setup involves adjusting parameters for best performance.
- The injection process fills the mold with molten plastic.
- Post-injection finishing includes trimming and quality control.
These steps are crucial for producing high-quality plastic parts.
How Do I Get Started With Injection Molding?
To get started with injection molding, begin by understanding the fundamentals of the process. This includes mold design, resin selection, and machine setup. Familiarize yourself with material preparation steps like resin drying, blending, and loading.
Learn the injection process of feeding molten plastic into the mold cavity, cooling, and ejection. Post-injection, address any defects like sink marks or warping. Quality control checks are crucial throughout the process to guarantee successful outcomes.
What Are the 4 Stages of Injection Molding?
The four stages of injection molding are:
- Mold preparation involves ensuring the mold is clean, inspected, and any damages are repaired for proper material flow.
- Material preparation includes selecting the appropriate resin, drying, blending, granulating, and loading it into the machine hopper.
- The injection process entails feeding molten plastic into the mold cavity under high pressure, allowing it to cool and solidify.
- Post-injection steps address issues like sink marks, flash, warping, trimming, finishing, and quality control checks.
What Is the Basic Knowledge of Injection Molding?
To comprehend the basic knowledge of injection molding, one must understand its fundamental principles:
- Material feeding
- Melting
- Injecting into a mold
- Cooling to achieve the final part
This process, widely utilized in industries such as automotive and medical devices, relies on precision and efficiency.
Mastery of injection molding basics is essential for the production of top-quality plastic components.
Conclusion
To wrap up, mastering injection molding requires a solid understanding of the process, design principles, resin selection, surface finishes, and quality systems. By following these steps meticulously, manufacturers can produce high-quality plastic parts efficiently and effectively.
Can you envision the endless possibilities of creating intricate and precise components through the art of injection molding?