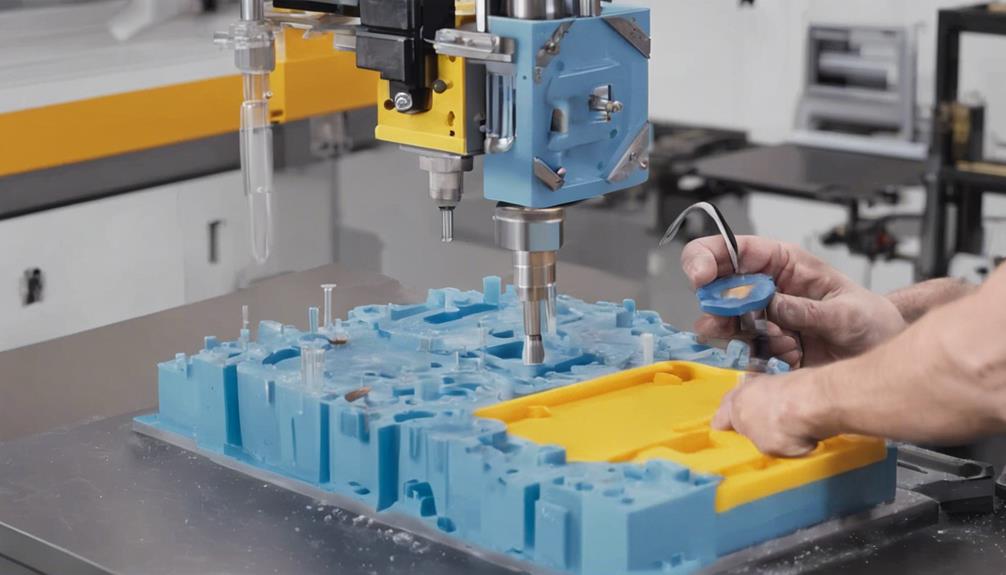
Injection moulding plastics is an essential manufacturing process where molten plastic resin is used to create intricate parts accurately. Understanding plastic materials like ABS, polycarbonates, and polyethylene is important due to their unique properties. This process involves high-pressure injection of melted plastic into molds, favored for high-volume production in various industries. Selecting the right material, mold type, and machine components are key to achieving consistent quality. Quality control, draft angles, and surface finishes play significant roles in producing high-quality products. Emphasizing mold design, controlling variables, and implementing quality measures are essential for achieving consistent part quality. Master the basics to excel in injection moulding plastics.
Basics of Injection Moulding Plastics
In the domain of injection molding plastics, understanding the fundamental basics of the process is paramount for achieving successful and precise production of plastic parts.
The production process begins with the careful selection of the appropriate plastic material. The chosen material, often in the form of resin pellets, is heated to a molten state within the injection unit. Once in a liquid state, the molten plastic is injected into a mold cavity under high pressure.
The mold plays a pivotal role in shaping the final product, as it defines the part's geometry and characteristics. The mold cavity is designed to be an exact negative of the desired part, ensuring accuracy and consistency in production.
Efficient cooling systems are employed to solidify the molten plastic within the mold, allowing for the timely ejection of the finished part.
Understanding the intricate interplay between material selection, mold design, and production parameters is essential for achieving high-quality plastic parts through injection molding.
Understanding Plastic Materials

Understanding the diverse characteristics and properties of plastic materials is essential in the domain of injection molding, as it directly influences the outcome and quality of the manufacturing process. Plastic materials used in injection molding primarily consist of thermoplastics such as ABS, polycarbonates, nylon, and polyethylene. Each type of plastic material offers unique properties including melting temperature, flow rate, and durability. Thermoplastics are favored in injection molding due to their capability to be reheated and recycled in the form of pellets, making them environmentally friendly options. The choice of plastic material plays a critical role in determining the quality, strength, and characteristics of the final molded product. A comprehensive understanding of these properties is crucial for selecting the most suitable plastic material for a specific injection molding project.
| Property | ABS | Polycarbonates | Nylon | Polyethylene |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Melting Temp | 200-240°C | 240-310°C | 190-260°C | 120-180°C |
| Flow Rate | High | Medium | High | Low |
| Durability | Good | Excellent | High | Excellent |
Injection Moulding Process Overview
The injection molding process entails the precise melting of plastic resin under high pressure and its subsequent injection into a mold cavity to create intricately designed plastic components.
Once the molten plastic is injected into the mold cavity, it solidifies to form the desired shape of the plastic part. This manufacturing technique is ideal for producing various products ranging from automotive components to medical devices and consumer goods.
Injection molding offers the advantage of being a versatile process capable of handling high production volumes while maintaining precise control over part dimensions. The cost-effectiveness of injection molding allows for the mass production of plastic parts with consistent quality and accuracy.
This process is favored in industries where efficiency, reliability, and scalability are key factors in manufacturing operations. By leveraging the benefits of injection molding, manufacturers can achieve efficient production processes that meet the demands of modern markets.
Types of Injection Moulds
Various types of injection molds play a crucial role in the manufacturing process. Each type offers distinct advantages and applications based on specific production requirements.
Steel molds, known for their durability, are commonly used in high-pressure injection molding processes due to their ability to withstand the rigors of manufacturing.
On the other hand, aluminum molds are preferred for short prototype runs or low-volume production. This is due to their cost-effectiveness and faster turnaround times.
MUD Frames, with their standard sizes facilitating quick mold changeovers, are popular for their versatility and efficiency in production setups.
Additionally, single cavity tools are designed to produce one part per cycle, making them suitable for low-volume production or prototyping applications.
Family tools are another type that enables the simultaneous production of multiple parts in a single molding cycle. This optimizes production efficiency and reduces manufacturing costs.
Each type of mold caters to specific production needs, offering manufacturers flexibility and efficiency in the injection molding process.
Injection Moulding Machine Components
Injection molding machine components encompass important elements such as the injection unit, clamping unit, control systems, and base, each playing a significant role in the plastic part production process.
| Component | Description | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Injection Unit | Melts and injects the plastic material into the mold cavity. | Responsible for heating, melting, and injecting the plastic material into the mold. |
| Clamping Unit | Holds the mold shut during injection and cooling, guaranteeing proper shaping and cooling of the plastic part. | Provides the force to keep the mold closed during the injection process and then opens the mold for part ejection. |
| Control Systems | Regulate process parameters such as temperature, pressure, and speed to ensure precise and repeatable production. | Monitor and control the various stages of the injection molding process, ensuring quality and consistency. |
Understanding the functions of each of these components is essential for achieving efficient and precise plastic part production. The synergy between the injection unit, clamping unit, and control systems is critical in guaranteeing the production of high-quality plastic parts.
Importance of Mold Design
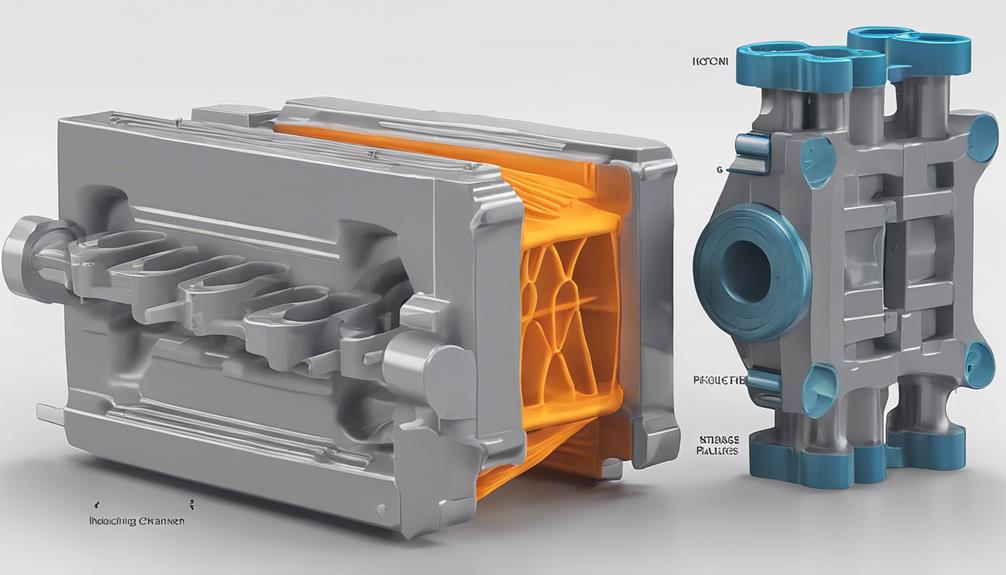
An integral aspect of successful injection molding processes lies in the meticulous attention to mold design considerations. Mold design plays a pivotal role in determining the quality of the final parts, the efficiency of production, and the overall cost-effectiveness of the process. Proper mold design encompasses various factors such as part geometry, wall thickness, draft angles, and the incorporation of cooling channels. These considerations are vital to guarantee that the molding process runs smoothly and yields high-quality plastic components.
The design of the mold directly impacts critical aspects of the injection molding process, including part shrinkage, potential warpage issues, and the dimensional accuracy of the final products. Engineers leverage mold design software and CAD tools to create intricate and optimized molds tailored to different types of plastic parts. By implementing effective mold design practices, manufacturers can achieve reduced cycle times, lower scrap rates, and enhanced part consistency throughout the injection molding operations.
Plastic Resins for Injection Moulding

Selecting the appropriate plastic resin is a vital decision in the injection molding process, as it directly influences the properties and characteristics of the final plastic components produced. Commonly used thermoplastic materials in injection molding include ABS, polycarbonate, nylon, polypropylene, and polyethylene. Each type of plastic resin offers unique properties such as impact resistance, heat resistance, flexibility, and chemical resistance.
Material selection plays a pivotal role in determining the desired part characteristics like strength, appearance, and durability. Factors such as cost, availability, and environmental impact also influence the choice of plastic resin for injection molding applications. Understanding the behavior of different plastic resins during the injection molding process is essential for successful part production, ensuring that the components meet the required specifications and standards.
Chemical resistance is particularly important in certain applications, where the final plastic parts need to withstand exposure to various chemicals without degradation or structural compromise.
Achieving Quality Surface Finishes

Understanding the significance of achieving quality surface finishes is paramount in enhancing the overall aesthetic appeal and functionality of plastic components produced through injection molding. Surface finishes in injection molding play a crucial role in determining the final look, feel, and performance of plastic parts. Techniques such as ultrasonic welding and laser engraving are utilized to create precise and detailed surface finishes, ranging from smooth to textured. Different surface finishes not only enhance aesthetics but also improve the functionality and durability of plastic components. Injection molding enables the production of consistent and high-quality surface finishes, meeting specific design requirements and customer expectations. Proper selection of surface finishing techniques is essential for achieving the desired results and ensuring the overall quality of injection molded products.
| Surface Finish Types | Description |
|---|---|
| Smooth | Shiny and reflective surface |
| Textured | Matte finish with patterns |
| Glossy | High sheen and smooth surface |
| Matte | Low sheen and non-reflective |
| Patterned | Specific designs or textures |
Quality Control in Injection Moulding

Quality control in injection molding is a critical aspect of the manufacturing process that guarantees adherence to design specifications and overall product quality. First Article Inspection (FAI) plays an important role in quality control by thoroughly examining the initial parts produced to make sure they meet the required standards. Additionally, the implementation of PPAP (Production Part Approval Process) is essential for verifying production processes and part quality through a standardized approach.
To maintain quality standards, industries such as medical devices often rely on quality control systems like ISO 13485 to meet regulatory requirements. Additionally, scientific molding techniques are utilized to ensure consistent quality and minimize variations in the injection molding process. By incorporating these rigorous quality control measures, manufacturers can produce high-quality parts that meet design specifications and adhere to industry standards, ultimately ensuring customer satisfaction and product reliability.
Guidelines for Draft Angles
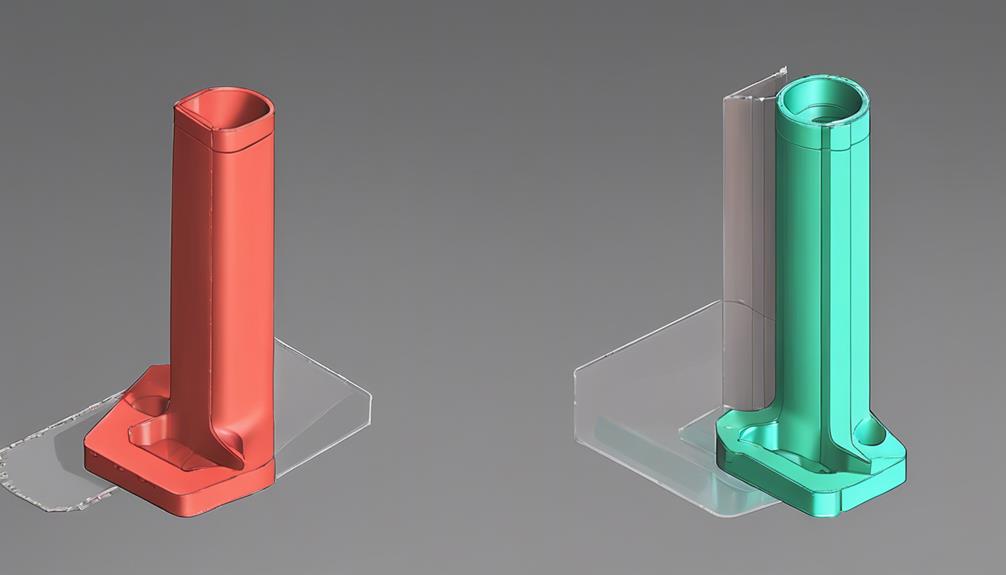
Draft angles play an important role in injection molding processes as they aid in the easy removal of molded parts. Maintaining an ideal draft angle, typically ranging from 1 to 3 degrees per side, is essential to prevent issues like part sticking or mold damage.
Designers must carefully consider draft angles early on to guarantee smooth ejection, cost-effectiveness, and dimensional accuracy of the final product.
Importance of Draft Angles
To ensure peak functionality and efficiency in injection molding processes, adherence to specified draft angles is essential for successful part ejection and quality production outcomes. Draft angles play a vital role in ensuring that parts can be easily released from the mold without sticking.
It is recommended to use draft angles of 1-3 degrees for vertical walls and 5-15 degrees for textured surfaces to facilitate smooth ejection. Failure to incorporate proper draft angles can result in part sticking within the mold cavity, leading to defects and production delays.
Optimal Draft Angle
For essential release of parts from injection molds, adherence to recommended draft angles is vital in guaranteeing smooth ejection and high-quality production outcomes. The ideal draft angle for injection molding typically ranges from 1 to 3 degrees, with larger parts potentially requiring up to 5 degrees to ensure easy release.
Inadequate draft angles can result in part sticking, damage, or increased friction during ejection, impacting manufacturing costs and part quality. Utilizing design software tools can assist in determining the best draft angles based on the specific part geometry and material properties.
Consistent attention to draft angles is crucial in injection molding to prevent issues during the ejection process and enhance overall production efficiency.
Draft Angle Design Tips
When designing molds for injection molding, meticulous attention to the angles of release is essential to guarantee seamless part ejection and uphold manufacturing efficiency. Draft angles, key design features in injection molding, facilitate easy ejection of molded parts from the mold cavity. Ideal draft angles typically range from 1 to 3 degrees, varying based on material, part complexity, and mold configuration.
Insufficient draft angles can lead to part sticking, damage, or increased production costs requiring manual intervention. These angles help reduce friction during ejection, minimize cosmetic defects, and ensure consistent part quality. Proper draft angle design is vital for efficient injection molding processes, contributing to long-term cost savings in production.
Selecting Thermoplastic Materials

Selecting the appropriate thermoplastic materials plays a pivotal role in determining the overall success and functionality of an injection molding project. When choosing thermoplastic materials, factors such as strength, flexibility, chemical resistance, and heat resistance must be carefully evaluated to guarantee the desired performance of the final product. Common thermoplastics like ABS, polycarbonate, polypropylene, and nylon are favored in injection molding due to their versatility and cost-effectiveness. These materials offer a balance of properties that make them suitable for a wide range of applications. Understanding the properties and limitations of different thermoplastic materials is crucial for selecting the most suitable material for a specific injection molding project. Below is a table outlining the properties of some commonly used thermoplastic materials:
| Thermoplastic Material | Strength | Flexibility | Chemical Resistance | Heat Resistance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ABS | High | Moderate | Good | Moderate |
| Polycarbonate | High | Low | Excellent | High |
| Polypropylene | Moderate | High | Good | Low |
| Nylon | High | High | Good | Moderate |
Ensuring Repeatable Part Function

Ensuring consistency in part functionality during injection molding necessitates meticulous control of critical process variables such as temperature, pressure, and cooling time. Proper mold design is essential to maintaining consistent part dimensions, alongside material selection and machine settings. By optimizing these factors, manufacturers can achieve repeatable part function.
Implementing quality control measures is also vital for ensuring reliable performance. Regular inspections, part testing, and process monitoring help in identifying any deviations that could affect part functionality. Utilizing scientific molding principles further aids in refining process parameters to minimize variations and enhance part quality.
Verification of part functionality through rigorous testing protocols and validation procedures is imperative for guaranteeing reliable performance in production. By focusing on mold design, process variables, and quality control, manufacturers can achieve the desired level of repeatability in part functionality, leading to high-quality injection-molded products.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are the Basics of Plastic Injection Molding?
Plastic injection molding basics involve injecting molten plastic into a mold cavity, allowing it to cool and solidify, resulting in high-precision plastic parts. Critical components like shot size, determining plastic volume, and sprue, the entry point, are essential.
Cooling channels in the mold aid in material cooling and hardening, ensuring part integrity. Machines with units such as injection, clamping, control, and base are vital for the process's success.
How Do I Get Started With Injection Molding?
To get started with injection molding, it's important to first explore the various plastic resins suitable for the process. Some common options include ABS, polycarbonate, and polypropylene. Understanding key mold design principles, such as wall thickness and draft angles, is essential for successful molding.
Familiarizing yourself with injection molding machine components and the sequential process steps is also crucial. Online resources and tutorials can provide foundational knowledge to help you grasp these fundamentals. This understanding is a key starting point for embarking on a successful injection molding journey.
What Is the Rule of Thumb for Injection Molding?
In injection molding, a fundamental rule of thumb is to maintain consistent wall thickness throughout the part to prevent defects like warping and sink marks. Design guidelines generally recommend a wall thickness of 2-3mm for best flow and cooling.
Deviating from this range can lead to challenges such as uneven filling with thin walls below 1mm or longer cooling times and shrinkage issues with thick walls exceeding 4-5mm. Adhering to this rule optimizes part quality, mold efficiency, and production costs.
Is Plastic Injection Molding Difficult?
Is plastic injection molding difficult?
Like a symphony conductor harmonizing various instruments, injection molding orchestrates design, material, and machine elements. Mastery demands meticulous attention to tolerances, wall thickness, draft angles, and material properties. Skilled professionals troubleshoot issues and optimize production efficiency. Continuous learning and adaptation to new technologies are essential.
While challenging, injection molding presents vast opportunities for innovation and mass production across diverse industries.
Conclusion
To sum up, mastering the art of injection moulding plastics requires a deep understanding of plastic materials, the injection moulding process, and quality control measures.
By selecting the right thermoplastic materials and following guidelines for draft angles, one can guarantee repeatable part function.
As the saying goes, 'practice makes perfect', so continuous improvement and attention to detail are key in achieving success in injection moulding.